St. Louis writer Michele Andrea Bowen made a splash in the inspirational fiction world with her Church Folk series, which followed the loves and losses of a tight-knit church community in Durham, North Carolina. Her latest release, Pastor Needs a Boo, launches a spin-off of that series, the Pastor’s Aide Club, and matches reader favorite Denzelle Flowers—a former FBI agent turned pastor—with the woman who will be the making of him. In a behind-the-book essay, Bowen explains why she chose Reverend Flowers to kick things off.
I always have a hearty “laugh out loud” moment when I think about how this book came to be. Pastor Needs a Boo is the book behind the books Up at the College and More Church Folk. The main characters in this story (and in the forthcoming books in the Pastor’s Aide Club Series) are the secondary characters readers were immensely interested in throughout the original series of Church Folk novels.
Every time I wrote a new novel, my readers would ask: “Sooooo, what about Denzelle Flowers?” They wanted to know things like “Is Denzelle ever going to settle down with a good woman?” “You know, I always thought he had a thing for . . . what’s her name . . . yeah, Marsha Metcalf.” “What happened to that pastor where the women in his church went wild, like ‘Church Girls Gone Wild’ during one of his Friday night services? Wasn’t that brother Denzelle?”
My readers wouldn't stop asking, “Is Reverend Denzelle Flowers ever going to settle down with a good woman and leave those hoochies alone?”
And “Is Reverend Denzelle Flowers ever going to settle down with a good woman and leave those hoochies alone?”
Who knew that my characters would touch the hearts and funny bones of my readers to the point of them having that good old “church folk” community connection with Denzelle and the other supporting characters like they were their cousins or something? And honestly, I was beginning to ask myself what was going on in Denzelle’s world. I always liked this character—he had a lot of “old school swag” and was very funny with regard to his approach to life.
Denzelle Flowers was the kind of man that a woman writing about love and the perils of the heart could explore, analyze and investigate. Why would a man with such a deep secret desire for true love run from it like it was some kind of sci-fi concocted nuisance? I also wanted to know what kind of woman would make this man stop running. In asking that question, I became more and more intrigued by another supporting character, Marsha Metcalf.
It was so much fun to get all up in Denzelle’s “grille.” Or, to be more exact, I had a good time digging in the brother’s history, finding out what happened to make him so jaded, and how a woman could be the inspiration to turn his life around. I wanted to know why men in a certain age group ran from the very thing that would actually give their hearts the joy they craved in all of the wrong ways. Well, what I really wanted to know, was why would a handsome, smart, smooth and savvy FBI Agent/preacher like Denzelle Flowers always found himself lookin’ for luuuuvvvv in all the wrong places.
Funny thing—that was the secret question on the hearts, minds and lips of my readers. They just didn’t “get” Denzelle Flowers. They couldn’t understand how he could be such good friends with the happily married Rev. Obadiah Quincey and his wife, Lena, and not believe that love really existed, that there really was a “Ruth” out their waiting to connect with her “Boaz.”
Yes, Denzelle Flowers definitely wanted to connect with a Ruth. He didn’t want the modern-day version of a Queen Esther, or a Rahab, or even Lazurus and Martha’s sister, Mary. Denzelle wanted that sweet, dedicated, smart, hard-working and good-looking Ruth. And just like Boaz, Denzelle needed the chance to watch and observe from afar, to act like he wasn’t thinking and feeling what the readers all knew he was thinking and feeling, and to stay safe while his heart did a soft whirring motion every time he witnessed his Ruth—Marsha—laboring in the field of activities created by his church’s Pastor’s Aide Club.
I had so much fun working with these characters and figuring out how to get this pastor from “needing a boo” to grabbing that boo close to his very fragile and needy heart.













 I realized Maeve was a mythological figure, but I’d learned that the Irish often made myths of their history and history of their myths, so making distinctions seemed less important than exploring the women who existed in the collective imagination of Ireland—goddesses and abbesses, saints and scholars, poets and queens. Many were listed in medieval Irish manuscripts in sections entitled “Ban Senchus,” a kind of “Let-us-now-praise-famous-women” litany that inspired me to look for such figures in my own life past and present.
I realized Maeve was a mythological figure, but I’d learned that the Irish often made myths of their history and history of their myths, so making distinctions seemed less important than exploring the women who existed in the collective imagination of Ireland—goddesses and abbesses, saints and scholars, poets and queens. Many were listed in medieval Irish manuscripts in sections entitled “Ban Senchus,” a kind of “Let-us-now-praise-famous-women” litany that inspired me to look for such figures in my own life past and present.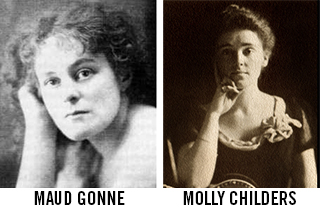 Nora finds that the female figures in early Irish literature inspired these women to leave behind the assumptions of their privileged backgrounds and join the struggle for Irish independence and women’s rights. She becomes part of a sisterhood that includes poets such as Ethna Carbery and Alice Milligan, along with a range of activists, suffragists and labor leaders, as well as a crippled American woman, Molly Childers, who sailed a load of guns past the British naval blockade in 1914 to arm Irish volunteers. There is not a sad sack among them.
Nora finds that the female figures in early Irish literature inspired these women to leave behind the assumptions of their privileged backgrounds and join the struggle for Irish independence and women’s rights. She becomes part of a sisterhood that includes poets such as Ethna Carbery and Alice Milligan, along with a range of activists, suffragists and labor leaders, as well as a crippled American woman, Molly Childers, who sailed a load of guns past the British naval blockade in 1914 to arm Irish volunteers. There is not a sad sack among them.

















